AI became a catch-all term that refers to any computer program that automatically does something. Many people make referrals to AI without actually knowing what it really means. There is public debate on whether it is an evil or savior for humanity. Thus this is yet another attempt to compile explain the introductory AI/ML concepts to go beyond this buzz for non-practitioners and curious people.
Artificial intelligence as an academic discipline was founded in 50s. Actually the “AI” term was coined by John McCarthy, an American computer scientist, back in 1956 at The Dartmouth Conference. According to John McCarthy, AI is "The science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs"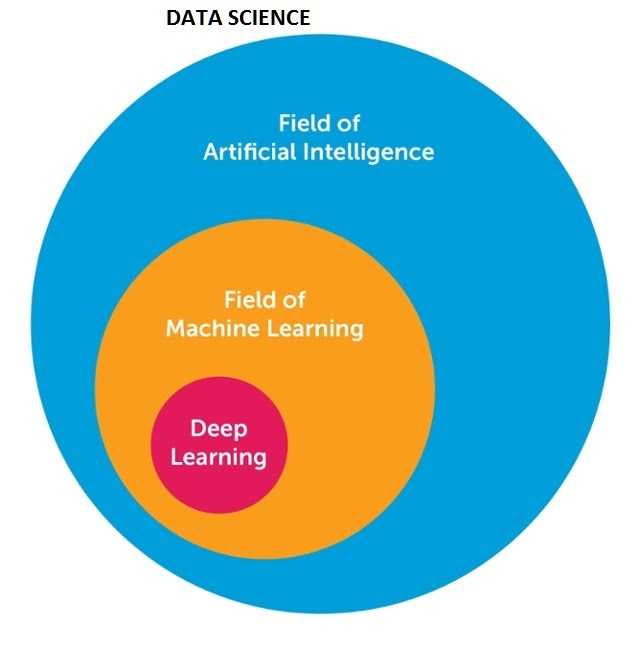
Artificial Intelligence is a way of making a computer, a computer-controlled robot, or a software think intelligently, in the similar manner the intelligent humans think.
AI is accomplished by studying how human brain thinks, and how humans learn, decide, and work while trying to solve a problem, and then using the outcomes of this study as a basis of developing intelligent software and systems.
Philosophy of AI
While exploiting the power of the computer systems, the curiosity of human, lead him to wonder, “Can a machine think and behave like humans do?”
Thus, the development of AI started with the intention of creating similar intelligence in machines that we find and regard high in humans.
Goals of AI
To Create Expert Systems − The systems which exhibit intelligent behavior, learn, demonstrate, explain, and advice its users.
To Implement Human Intelligence in Machines − Creating systems that understand, think, learn, and behave like humans.
What is the difference between Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL)?
While people often use these terms interchangeably, I think below is a good conceptual depiction to differentiate these 3 terms. AI is really a broad term and somewhat this also causes every company to claim their product has AI these days Then ML is a subset of AI, and consists of the more advanced techniques and models that enable computers to figure things out from the data and deliver AI applications. ML is the science of getting computers to act without being explicitly programmed
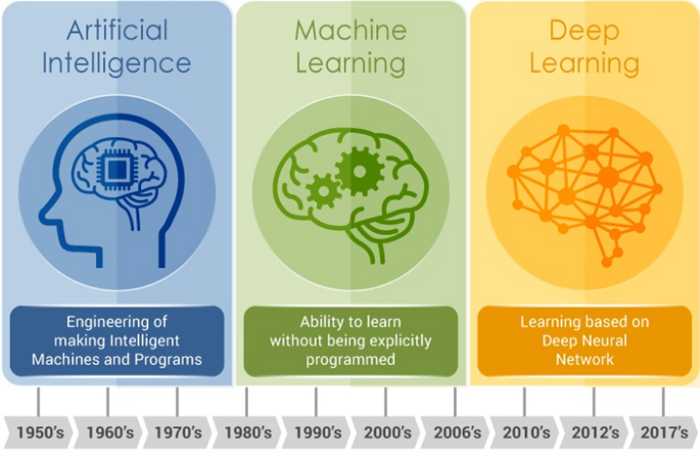
Finally, DL is a newer area of ML that that uses multi-layered artificial neural networks to deliver high accuracy in tasks such as object detection, speech recognition, language translation and other recent breakthroughs that you hear in the news. Beauty and strength of DL is they can automatically learn/extract/translate the features from data sets such as images, video or text, without introducing traditional hand-coded code or rules.
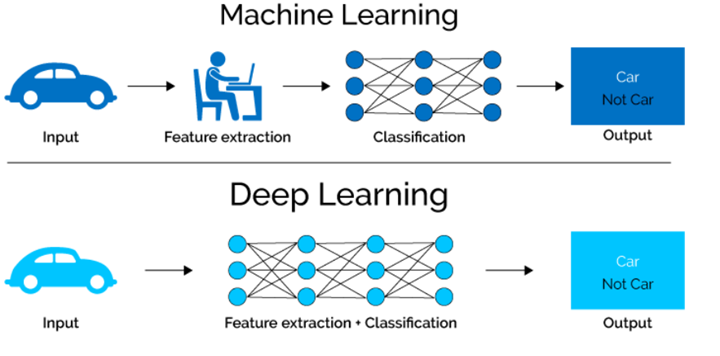
In Machine Learning there are different models that generally fall into 3 different categories: (1)Supervised learning, (2) UnSupervised learning and (3) Reinforcement learning.
Supervised learning: Involves an output label associated with each instance in the dataset. This output can be discrete/categorical (red, dog, panda, ford mustang, STOP sign, spam…) or real-valued. Right now, almost all learning is supervised. Your data has known labels as output. It involves a supervisor that is more knowledgeable than the neural network itself. For example, the supervisor feeds some example data about which the supervisor already knows the answers. The supervisor guides the system by tagging the output. For example, a Supervised machine learning system that can learn whcih emails are 'spam'and which are 'not spam' The algorithm would be first trained with available input data set (of zillions of emails) that is already tagged with this classification to help the machine learning system learn the characteristics or parameters of the ‘spam’ email and distinguish it from those of ‘not spam’ emails. Just as a three-year-old learns the difference between a ‘block’ and a ‘soft toy’, the supervised machine learning system learns which email is ‘spam’ and which is ‘not spam’. Techniques such as linear or logistic regressions and decision tree classification fall under this category of learning.
Regression: This is a type of problem where we need to predict and forecast for the continuous-response values. Some examples are what is the price of house in a specific city with 3 bedrooms and above 2,000 sqft? Predicting financial results, stock prices or how many total runs can be on board in a cricket game. You have an existing data set outputs (supervised learning) and your algorithm predicts the outcome based on a fitting function.
Classification: Where you need to categorize a certain observation into a group. In the below picture, if you’re given a dot you need to classify it as either a blue dot or a red dot. Few more examples would be — to predict if a given email is spam or not spam? Assigning a certain news article into a group — like sports, weather, or science. Will it rain today or not? Is this picture a cat or not? Detecting fraud or evaluating risk for frauds or insurance under writing.
2. Unsupervised Learning — This is an ‘unaided’ type learning when your data typically has no known output labels or any feedback loop. This is useful when there is no example data set with known answers and your are searching for a hidden pattern. In this case, clustering i.e. dividing a set of elements into groups according to some unknown pattern is carried out based on the existing data sets. The system has to understand itself from the data set we provide. In general, unsupervised learning is a bit difficult to implement and thus it’s not used as widely as supervised learning. Most popular types are clustering and association as below.
Clustering: This is a type of unsupervised learning problem where we group similar things together. Some examples are: Given news articles or books, cluster them into different types of themes. Given a set of tweets, cluster them based on content of tweet. Could also be used for politics, health care, shopping, real estate etc.
3. Reinforcement Learning (RL)− Now instead of telling the child which toy to put in which box, you reward the child with a ‘big hug’ when the child makes the right choice or you make a ‘sad face’ when the child makes the wrong action. Very quickly after a few iterations the child learns which toys need to go into which box — this is called ReinForcement Learning. Systems are trained by receiving virtual “rewards” or “punishments”, essentially learning by trial and error.
Applications of AI
AI has been dominant in various fields such as −
Gaming − AI plays crucial role in strategic games such as chess, poker, tic-tac-toe, etc., where machine can think of large number of possible positions based on heuristic knowledge.
Natural Language Processing − It is possible to interact with the computer that understands natural language spoken by humans.
Expert Systems − There are some applications which integrate machine, software, and special information to impart reasoning and advising. They provide explanation and advice to the users.
Vision Systems − These systems understand, interpret, and comprehend visual input on the computer. For example,
A spying aeroplane takes photographs, which are used to figure out spatial information or map of the areas.
Doctors use clinical expert system to diagnose the patient.
Police use computer software that can recognize the face of criminal with the stored portrait made by forensic artist.
Speech Recognition − Some intelligent systems are capable of hearing and comprehending the language in terms of sentences and their meanings while a human talks to it. It can handle different accents, slang words, noise in the background, change in human’s noise due to cold, etc.
Handwriting Recognition − The handwriting recognition software reads the text written on paper by a pen or on screen by a stylus. It can recognize the shapes of the letters and convert it into editable text.
- Intelligent Robots − Robots are able to perform the tasks given by a human. They have sensors to detect physical data from the real world such as light, heat, temperature, movement, sound, bump, and pressure. They have efficient processors, multiple sensors and huge memory, to exhibit intelligence. In addition, they are capable of learning from their mistakes and they can adapt to the new environment.
Conclusion
I think machine and deep learning, like data science in general, is as much art as science. When you start studying the AI field, your head may turn in the beginning about models, data sets, methods and all. I would encourage to pick a favorite ML domain and going deeper. It is computer vision for me these days. The fluency only comes with practice like everything else in life.
We will see many more news and inventions in AI domain in 2020. I also expect to see more advances and applied cases at the “edges” for ML to be available with mobile phones, ear buds, watches and other portable devices beyond high power computers only. So beware for more!
I would like to finish with one of my favorite quotes from Satya Nadella “I believe in a world that will have an abundance of artificial intelligence, but what will be scarce is real intelligence and human qualities, like empathy. I think great innovation comes from the empathy you have for the problems you want to solve for people.”