In the rapidly evolving landscape of construction and architecture, BIM technology stands as a cornerstone for digital transformation. We delve into the future of BIM technology, exploring how artificial intelligence, automation, and the metaverse are poised to redefine building information modeling practices. As industries adapt to digital demands, BIM technology integrates these advanced tools to enhance efficiency, collaboration, and innovation. Our exploration uncovers the synergies that will propel BIM forward, ensuring projects are not only designed but also experienced in virtual realms before physical realization.
- Historical Evolution of BIM Technology
- Current State of BIM Technology in Industry
- The Integration of AI in the Future of BIM Technology
- Advancements in Automation for BIM Workflows
- Exploring the Metaverse in BIM Technology
- Synergies of AI, Automation, and Metaverse in BIM
- Challenges in Adopting Advanced BIM Technology
- Case Studies Demonstrating the Future of BIM Technology
- Predictions for the Next Decade in BIM Technology
- Conclusion on the Future of BIM Technology
- Suggestions / Recommendations
- 15 FAQs with Answers
Building information modeling, or BIM, has transitioned from a mere drafting tool to a comprehensive data ecosystem. We observe that the future of BIM technology hinges on seamless integration with AI for predictive analytics, automation for streamlined workflows, and the metaverse for immersive simulations. This convergence promises to minimize errors, reduce costs, and accelerate project timelines. Professionals in architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) sectors must embrace these advancements to stay competitive. Through detailed analysis, we highlight how these elements intertwine, offering a roadmap for implementation.
The global BIM market, valued at over $7 billion in 2023, is projected to exceed $15 billion by 2030, driven by technological infusions. We emphasize that understanding the future of BIM technology requires examining each component’s role. AI brings intelligence to data processing, automation eliminates repetitive tasks, and the metaverse creates collaborative virtual spaces. Together, they form a trifecta that transforms traditional BIM into a dynamic, intelligent system capable of handling complex urban developments and sustainable designs.
Historical Evolution of BIM Technology
To appreciate the future of BIM technology, we must first trace its origins. BIM emerged in the 1970s with early computer-aided design systems, but it gained traction in the 2000s through standards like IFC (Industry Foundation Classes). We note that initial adop focused on 3D modeling, allowing architects to visualize structures beyond 2D blueprints. By the 2010s, BIM incorporated 4D (time) and 5D (cost) dimensions, enabling better project management.
Governments worldwide mandated BIM for public projects, such as the UK’s 2016 Level 2 requirement, fostering widespread adoption. We see how software like Autodesk Revit and Bentley Systems revolutionized workflows, integrating data from multiple stakeholders. Challenges like interoperability issues were addressed through open standards, paving the way for cloud-based BIM platforms. Today, BIM encompasses 6D (sustainability) and 7D (facility management), setting the stage for AI-driven enhancements.
In recent years, the pandemic accelerated digital shifts, with remote collaboration tools embedding into BIM. We explore case studies like the Sydney Opera House retrofit, where BIM models facilitated precise renovations. This evolution underscores the need for forward-thinking strategies, where AI, automation, and the metaverse build upon these foundations to create resilient, adaptive systems.
Current State of BIM Technology in Industry
Presently, BIM technology is integral to AEC workflows, with over 70% of large firms utilizing it for clash detection and coordination. We analyze how tools like Navisworks simulate construction sequences, preventing on-site conflicts. Cloud platforms such as BIM 360 enable real-time data sharing, reducing project delays by up to 20%. Sustainability features allow energy modeling, aligning with green building certifications like LEED.
However, limitations persist, including data silos and skill gaps among professionals. We discuss how current BIM relies heavily on manual inputs, leading to inefficiencies. Integration with IoT devices for real-time monitoring is emerging, but scalability remains a hurdle. In manufacturing, BIM supports prefabrication, optimizing material use and minimizing waste.
Globally, regions like Europe lead in BIM maturity, with mandates driving innovation. We highlight Asia’s rapid growth, fueled by urbanization, where BIM aids in smart city developments. North America’s focus on infrastructure renewal incorporates BIM for asset management. This snapshot reveals opportunities for AI to automate data analysis, automation to streamline processes, and the metaverse to enhance virtual interactions.
The Integration of AI in the Future of BIM Technology
AI is revolutionizing the future of BIM technology by infusing intelligence into every phase of building lifecycle management. We examine how machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets from BIM models to predict structural integrity, optimizing designs before construction begins. For instance, AI-powered generative design tools, like those in Autodesk’s ecosystem, generate thousands of iterations based on parameters such as cost, materials, and environmental impact, selecting the most efficient options.
Predictive maintenance emerges as a key application, where AI processes sensor data from embedded IoT devices to forecast equipment failures, extending asset longevity. We delve into natural language processing (NLP) capabilities that interpret regulatory documents, ensuring BIM compliance automatically. Computer vision enhances quality control by scanning construction sites via drones, comparing real-time images against BIM models to detect deviations.
In urban planning, AI simulates traffic flows and energy consumption within BIM frameworks, supporting sustainable city designs. We discuss ethical considerations, such as bias in AI algorithms, and advocate for diverse training data. Case studies from projects like the Hudson Yards development in New York illustrate AI reducing design time by 30%. As AI evolves, its role in the future of BIM technology will include autonomous decision-making, where systems suggest modifications in real-time during construction.
Deep learning models are being trained on historical BIM data to anticipate risks, such as seismic vulnerabilities, integrating geospatial information for accurate simulations. We explore reinforcement learning, where AI agents learn optimal construction sequences through trial and error in virtual environments. This not only accelerates projects but also minimizes environmental footprints by optimizing resource allocation.
Furthermore, AI facilitates personalized architecture, adapting designs to user preferences gleaned from behavioral data. In healthcare facilities, AI-enhanced BIM models simulate patient flows, improving layouts for efficiency and safety. We anticipate quantum computing integrations, enabling complex simulations unattainable with classical systems. Overall, AI positions the future of BIM technology as proactive rather than reactive, driving unprecedented innovation.
Advancements in Automation for BIM Workflows
Automation is a pivotal force in the future of BIM technology, eliminating manual drudgery and enhancing precision. We investigate robotic process automation (RPA) tools that handle repetitive tasks like data entry and report generation within BIM software. For example, scripts in Dynamo automate parametric modeling, allowing rapid adjustments to building elements based on changing requirements.
On construction sites, automated machinery like 3D printers and robotic arms fabricate components directly from BIM models, reducing labor costs and errors. We highlight prefabrication factories where automation lines produce modular units, assembled on-site with minimal human intervention. Digital twins, virtual replicas synced with physical assets, leverage automation for continuous monitoring and adjustments.
Workflow orchestration platforms integrate BIM with ERP systems, automating procurement and scheduling. We discuss how APIs enable seamless data flow between tools, such as linking BIM to project management software like Procore. In facility management, automation scripts trigger maintenance alerts based on BIM data thresholds, optimizing operations.
Challenges include cybersecurity risks in automated systems, which we address through blockchain for secure data transactions. Case studies from the Crossrail project in London demonstrate automation cutting timelines by 15%. As automation advances, it will incorporate adaptive learning, where systems self-optimize based on project feedback, solidifying its place in the future of BIM technology.
Industrial robots equipped with BIM-integrated vision systems perform precise installations, such as HVAC systems, with millimeter accuracy. We explore swarm robotics, where multiple units collaborate on tasks like surveying large sites, feeding data back into BIM models. Automation in documentation generates as-built models automatically, ensuring accuracy for future renovations.
In sustainable practices, automation optimizes energy models by simulating scenarios and selecting low-carbon options. We foresee fully automated design-to-construction pipelines, where BIM serves as the central nervous system. This shift demands upskilling workforces, focusing on oversight rather than execution.
Exploring the Metaverse in BIM Technology
The metaverse represents a transformative dimension in the future of BIM technology, creating immersive virtual worlds for collaboration and simulation. We define the metaverse as interconnected digital spaces where users interact via avatars, extending BIM beyond static models. Platforms like Decentraland and Roblox are precursors, but AEC-specific metaverses like NVIDIA Omniverse enable real-time BIM rendering.
Stakeholders can walk through virtual buildings, identifying issues early. We examine how VR headsets integrate with BIM for design reviews, allowing remote teams to collaborate as if in the same room. Augmented reality (AR) overlays BIM data on physical sites, guiding workers during construction.
In training, the metaverse simulates hazardous scenarios without risk, enhancing safety protocols. We discuss asset tokenization via NFTs in the metaverse, facilitating virtual property sales before physical completion. Challenges like data privacy are mitigated through decentralized ledgers.
Case studies from the NEOM project in Saudi Arabia showcase metaverse-enhanced BIM for city-scale planning. As bandwidth improves, the metaverse will support hyper-realistic simulations, including environmental interactions like wind and light.
Social aspects allow community input on designs, fostering inclusive urban development. We predict hybrid events where physical and virtual participants engage with BIM models simultaneously. This integration elevates the future of BIM technology to experiential levels.
Synergies of AI, Automation, and Metaverse in BIM
The true power in the future of BIM technology lies in the interplay between AI, automation, and the metaverse. We illustrate how AI analyzes data within metaverse environments, automating optimizations in real-time. For instance, AI algorithms in virtual spaces predict user behaviors, automating design adjustments.
Automated workflows populate metaverse models with AI-generated content, such as furniture placements based on ergonomic data. We explore collaborative scenarios where global teams use AI-assisted avatars in the metaverse to automate conflict resolutions in BIM.
In supply chain management, AI forecasts material needs, automation handles orders, and the metaverse visualizes logistics. This triad reduces project overruns by integrating predictive, executive, and immersive elements.
Ethical frameworks ensure equitable access, with AI detecting biases in automated processes within virtual realms. We anticipate ecosystems where these technologies evolve symbiotically, driving BIM toward autonomy.
Challenges in Adopting Advanced BIM Technology
Despite the immense promise offered by the future of BIM technology infused with AI, automation, and the metaverse, widespread adoption encounters significant hurdles that demand strategic attention. We examine these challenges in depth, drawing from industry reports, academic studies, and real-world implementations to provide a comprehensive understanding.
Interoperability Issues Between Tools and Legacy Systems
One of the foremost barriers in advancing BIM technology is interoperability—the seamless exchange of data across diverse software platforms, tools, and legacy systems. Many organizations still rely on older BIM models and proprietary formats that do not easily integrate with modern AI-driven tools or metaverse platforms. For instance, converting traditional BIM models into immersive extended reality (XR) environments for the metaverse requires sophisticated mapping and often results in data loss or inaccuracies.
Studies highlight that hardware and software interoperability remains a major challenge, particularly when migrating BIM to metaverse applications. Legacy systems, built on standards like older IFC versions, struggle to communicate with AI algorithms that demand rich, semantic data. This fragmentation leads to silos, duplicated efforts, and increased project risks. We recommend adopting standardized APIs and open formats such as openBIM and IFC4 to bridge these gaps. Industry leaders like Autodesk and Bentley are advancing interoperability through cloud-based platforms, enabling smoother data flow between AI tools and BIM ecosystems.
Furthermore, integrating automation scripts with existing BIM workflows often encounters compatibility issues, where robotic process automation (RPA) tools fail to interpret nuanced model data from disparate sources. Addressing this requires robust middleware solutions and ongoing standardization efforts from bodies like buildingSMART International.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
As BIM technology evolves with AI and metaverse integrations, data security emerges as a critical challenge. Automated systems and immersive virtual environments handle vast amounts of sensitive project data, including intellectual property, structural details, and personal stakeholder information. In metaverse applications, real-time collaboration exposes data to cyber threats, with concerns over privacy in virtual spaces and potential breaches during data transmission.
Research points to implementation costs, data security, and interoperability as primary obstacles in BIM-to-metaverse transitions. Robust encryption protocols, blockchain for immutable records, and zero-trust architectures are essential mitigations. We advocate for compliance with standards like GDPR and ISO 27001, alongside regular security audits to safeguard automated and metaverse-integrated BIM workflows.
Skill Shortages and Training Gaps
The rapid infusion of AI, automation, and metaverse technologies into BIM demands a workforce skilled in these domains, yet significant shortages persist. Professionals trained in traditional BIM may lack expertise in machine learning, VR/AR development, or automated scripting. This gap hinders effective implementation, leading to underutilization of advanced features.
Educational partnerships and targeted training programs are vital. We suggest collaborations with institutions to develop curricula covering AI in generative design, automation in workflows, and metaverse navigation. Certifications from platforms like Autodesk University can bridge these gaps, empowering teams to leverage the full potential of the future of BIM technology.
High Implementation Costs and Barriers for Small Firms
Initial costs for adopting advanced BIM features—such as AI software licenses, high-performance hardware for metaverse rendering, and automated robotics—can be prohibitive, especially for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Cloud-based subscriptions offer a scalable solution, reducing upfront investments while providing access to cutting-edge tools.
Regulatory Lags and Ethical Considerations
Regulatory frameworks often lag behind technological advancements, particularly in governing metaverse spaces and AI decision-making in BIM. Issues like liability for AI-generated designs or data governance in virtual collaborations require proactive advocacy. Ethical concerns, including bias in AI algorithms, must be addressed through diverse datasets and transparent processes.
Environmental Impacts of Supporting Infrastructure
The computational intensity of AI and metaverse applications relies on energy-hungry data centers, contributing to significant carbon footprints and water consumption for cooling. As BIM integrates these technologies, their environmental toll—including emissions from training AI models—must be mitigated through green computing initiatives, renewable energy sourcing, and efficient algorithms.
We emphasize sustainable practices, such as optimizing AI models for lower energy use and selecting eco-friendly data center providers, to align the future of BIM technology with global sustainability goals.
Case Studies Demonstrating the Future of BIM Technology
Real-world projects illustrate the transformative impact of integrating AI, automation, and emerging immersive technologies into BIM. We explore notable examples, highlighting successes, innovations, and lessons learned.
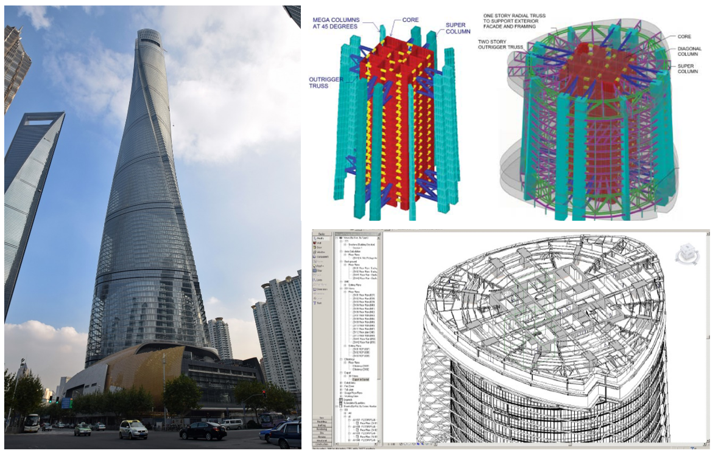
Shanghai Tower: Pioneering BIM for Sustainable High-Rise Construction
The Shanghai Tower, China’s tallest building at 632 meters, exemplifies advanced BIM implementation. Extensive use of Autodesk Revit and Navisworks enabled multidisciplinary coordination, clash detection, and performance simulations. BIM facilitated the tower’s unique twisting form, optimizing wind loads and reducing structural wind forces by 24%.
Although primarily pre-AI era, the project incorporated parametric modeling and energy simulations that laid groundwork for modern AI-optimized designs. Fabrication automation streamlined curtain wall production, reducing waste. Outcomes included significant energy savings and efficient construction sequencing.
This case demonstrates how BIM enhances sustainability and efficiency, paving the way for AI-enhanced iterations in future skyscrapers.
Apple Park Campus: Immersive Design Validation and Sustainability Focus
Apple Park, the iconic “spaceship” campus in Cupertino, leveraged advanced BIM for its curved architecture and vast green spaces. Foster + Partners utilized detailed 3D models for precise coordination of complex systems, including the world’s largest naturally ventilated building.
VR simulations allowed immersive design reviews, akin to early metaverse-like experiences, enabling stakeholders to “walk through” the campus virtually. AI-assisted tools optimized energy models, contributing to LEED Platinum certification.
The project showcases BIM‘s role in sustainable, collaborative design, with virtual prototyping reducing on-site changes.
Øresund Bridge: Drone Automation and Digital Monitoring
The Øresund Bridge, linking Denmark and Sweden, has employed drones for inspections, integrating with digital models for maintenance. AI analyzes drone-captured images to detect cracks, comparing against baseline data in a digital twin framework.
Automated UAV route planning using BIM-GIS data optimizes inspections, enhancing safety and efficiency.
This cross-border project highlights automation in infrastructure management, extending BIM into operational phases.
Additional cases, such as digital twins in modular construction and AI-driven quality control, further validate these advancements.
Predictions for the Next Decade in BIM Technology
Looking ahead to 2035, the future of BIM technology will be defined by deeper integration of AI, automation, and the metaverse, transforming the AEC industry.
By 2030, AI-driven generative design will become standard, producing optimized structures autonomously. Digital twins, synced with real-time IoT data, will enable predictive maintenance, reducing downtime by 30-50%.
Automation will see robots constructing 40-60% of buildings, guided by BIM models. The metaverse will serve as primary collaboration hubs, with immersive VR/AR for global teams.
Quantum computing may enable molecular-level simulations by 2035, revolutionizing material science within BIM.
Sustainability will drive carbon-neutral designs, with AI optimizing for zero-waste. Market growth projections indicate BIM adoption nearing 90% globally, fueled by mandates and efficiencies.
These predictions underscore a shift toward autonomous, immersive, and sustainable BIM ecosystems.
Conclusion on the Future of BIM Technology
As we conclude, the future of BIM technology—propelled by AI, automation, and the metaverse—heralds an era of unprecedented efficiency, sustainability, and innovation in the built environment. Overcoming challenges through collaboration and strategic adoption will unlock resilient, intelligent infrastructure for generations to come.
Suggestions / Recommendations
- Invest in AI training for BIM teams to leverage predictive tools.
- Adopt cloud-based automation platforms for seamless workflows.
- Explore metaverse prototypes for project visualizations.
- Prioritize data security in integrated systems.
- Collaborate with tech firms for custom solutions.
- Conduct regular audits for interoperability.
- Integrate sustainability metrics early in BIM processes.
- Use open standards to avoid vendor lock-in.
- Pilot hybrid AI–metaverse projects.
- Monitor regulatory changes affecting digital twins.
- Implement green computing for data-intensive AI and metaverse applications.
- Foster partnerships for skill development in emerging technologies.
- Utilize drones and IoT for real-time BIM updates.
- Embrace generative design for optimized outcomes.
- Develop ethical guidelines for AI in decision-making.
15 FAQs with Answers
- What is the role of AI in the future of BIM technology? AI enhances BIM by providing predictive analytics, generative design, and automated compliance checks, reducing errors and optimizing resources.
- How does automation impact BIM workflows? Automation streamlines repetitive tasks like modeling and documentation, improving efficiency and allowing focus on creative aspects.
- What benefits does the metaverse bring to BIM? The metaverse offers immersive collaboration, virtual simulations, and stakeholder engagement, making design reviews more interactive.
- Can AI and automation reduce construction costs in BIM? Yes, by predicting issues early and automating processes, they can cut costs by up to 25% through minimized rework.
- How is the metaverse integrated with existing BIM software? Through platforms like Omniverse, which sync BIM models in real-time for VR/AR experiences.
- What challenges exist in adopting AI for BIM? Key challenges include data quality, integration with legacy systems, and ethical concerns like algorithm bias.
- Is automation in BIM suitable for small projects? Absolutely, scalable tools like RPA can benefit even small-scale designs by saving time.
- How does BIM in the metaverse improve safety? It allows simulation of hazardous scenarios virtually, training workers without real-world risks.
- What future trends combine AI, automation, and metaverse in BIM? Synergies include AI-optimized automated designs visualized in metaverse environments.
- Can BIM technology with AI promote sustainability? Yes, by simulating energy-efficient models and optimizing material use.
- How do governments influence the future of BIM technology? Through mandates and funding for digital infrastructure projects.
- What skills are needed for BIM professionals in this future? Proficiency in AI tools, automation scripting, and metaverse navigation.
- Is the metaverse accessible for all BIM users? With improving hardware, yes, but initial costs may vary.
- How does automation handle BIM data security? Through encrypted protocols and blockchain for tamper-proof records.
- What is the projected growth of BIM technology? Expected to double in market size by 2030, driven by these advancements.




![Future of BIM Technology – AI, Automation, and the Metaverse 4 PDF] Title : BIM Applications in the Shanghai Tower Construction ...](https://figures.semanticscholar.org/e299d4eb7846da20479f4b679e171cab39360d67/5-Figure4-1.png)
![Future of BIM Technology – AI, Automation, and the Metaverse 6 PDF] Title : BIM Applications in the Shanghai Tower Construction ...](https://figures.semanticscholar.org/e299d4eb7846da20479f4b679e171cab39360d67/5-Figure5-1.png)










